Understanding the Basics of Node.js and its Architecture
Node.js is an open-source, cross-platform runtime environment that runs JavaScript code outside of a web browser. It is designed to build scalable network applications. This blog post will discuss the basics of Node.js and its architecture.
Node.js has rapidly gained popularity among developers for its efficiency and scalability in building high-performance web applications. In this blog post, we will delve into the basics of Node.js and explore its architecture. We’ll discuss how Node.js revolutionizes backend development, its key components, and the benefits it offers to developers. By the end, you’ll have a solid understanding of Node.js and its role in modern web development.
What is Node.js?
Node.js is an open-source, server-side JavaScript runtime environment that enables developers to build scalable and high-performance applications. Unlike traditional server-side languages, such as PHP or Java, which rely on multithreading, Node.js adopts an event-driven, non-blocking I/O model. This approach allows Node.js to handle a large number of concurrent connections efficiently.
Key Features and Benefits of Node.js:
Fast and Scalable: Node.js utilizes an event-driven, non-blocking architecture, which makes it incredibly fast and scalable. It can handle a massive number of simultaneous connections with relatively low resource consumption, making it ideal for building real-time applications and microservices.
JavaScript Everywhere: One of the major advantages of Node.js is that it allows developers to use JavaScript both on the client-side and server-side. This enables full-stack JavaScript development and allows for seamless code sharing between the front-end and back-end, reducing development time and effort.
Vibrant Ecosystem: Node.js has a vast and vibrant ecosystem of open-source packages and libraries available through npm (Node Package Manager). These packages offer ready-made solutions for common tasks, such as handling HTTP requests, working with databases, and implementing authentication, saving developers time and effort in building robust applications.
Node.js Architecture:
Node.js architecture consists of several key components that work together to provide its powerful capabilities. Let’s take a closer look at these components:
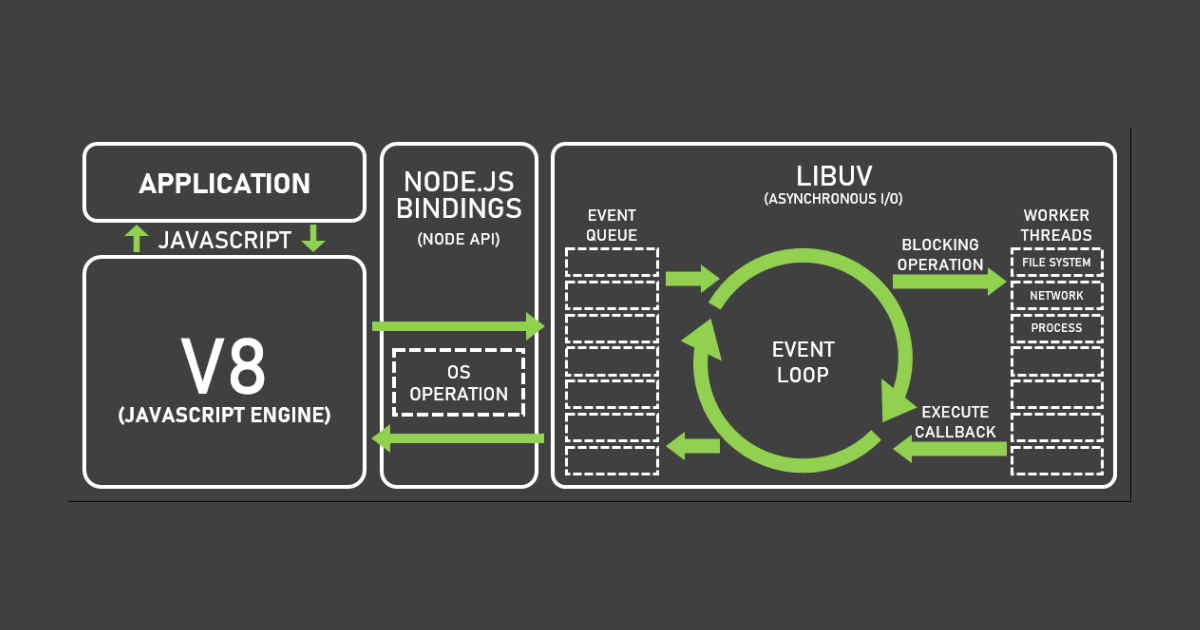
V8 Engine: Node.js is built on top of the V8 JavaScript engine, developed by Google. The V8 engine compiles JavaScript code into machine code, enabling high-performance execution.
Event Loop: The event loop is the heart of Node.js. It allows Node.js to handle asynchronous operations efficiently. Instead of waiting for a task to complete, Node.js registers a callback and continues to process other requests. Once the task completes, the event loop triggers the callback, allowing Node.js to move forward.
Libuv: Libuv is a cross-platform library that provides an event-driven, asynchronous I/O framework for Node.js. It handles all the asynchronous operations, such as file system operations and network requests, allowing Node.js to be non-blocking and highly performant.
Modules: Node.js follows a modular approach, allowing developers to break their code into reusable modules. Each module encapsulates a specific set of functionality, making it easier to manage and maintain large-scale applications.
HTTP and Core Modules: Node.js provides core modules for essential functionality, such as working with the file system, handling HTTP requests, and managing streams. These modules offer a solid foundation for building web servers and APIs.
Conclusion:
Node.js has revolutionized backend development with its efficient, event-driven architecture and extensive ecosystem. By leveraging JavaScript on the server-side, Node.js enables full-stack JavaScript development, simplifying code sharing and reducing development time. With its fast and scalable nature, Node.js has become a popular choice for building real-time applications and microservices. Understanding the basics of Node.js and its architecture lays a solid foundation for exploring its vast capabilities and building robust web applications.
So, dive into the world of Node.js, explore its powerful features, and unlock new possibilities in modern web development.